

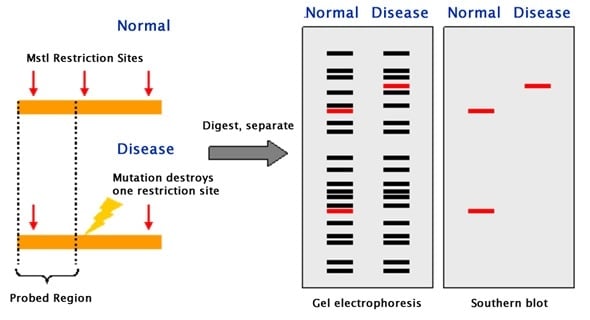
Mutations within the DNA result in strands of different lengths. Special enzymes that cleave the DNA in specific locations are used to digest strands of DNA. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 57(8), 1855–1867. RFLP, or restriction fragment length polymorphism, is a molecular biological technique used to compare DNA from two samples. Computer-simulated RFLP analysis of 16S rRNA genes: Identification of ten new phytoplasma groups. A high-density genetic map of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench based on 2926 AFLP®, RFLP and SSR markers. 54 RFLPs are visualized by digesting DNA from different individuals with a restriction enzyme, followed by gel electrophoresis to separate. Inverse PCR-based RFLP scanning identifies low-level mutation signatures in colon cells and tumors. A restriction fragment length polymorphism is defined by the existence of alternative alleles associated with restriction fragments that differ in size from each other. Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) (pronounced rif lip) is one of the earliest molecular markers developed for genetic mapping and one of the first techniques used for analysis in forensic science and several other fields. H., Kaur, M., Wang, G., Zhu, P., Zhang, Y., & Makrigiorgos, G. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Analysis. Australian Veterinary Journal, 78(3), 184–190. An RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) is a variation in the length of a specific restriction fragment excised from a chromosome by digestion. RFLPs are visualized by digesting DNA from different individuals with a restriction enzyme, followed by gel electrophoresis to separate fragments according to. DNA fingerprinting of Australian isolates of Mycobacterium avium subsp paratuberculosis using IS900 RFLP. This suggests that Spelta wheat originated from a hybridization between T. To determine the usefulness of polymerase chain reactionrestriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) in the identification and speciation. RFLP loci are much fewer in the D genome than in the A and B genomes, but the numbers of non-RFLP loci are nearly the same in these three genomes. This suggests the influence of gametic factors in those regions. RFLP, as a molecular marker, is specific to a single clone/restriction enzyme combination. The CS alleles on 4A exhibit preferential transmission, while those on 2D exhibit depressed transmission, compared with Spelta alleles. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) is a difference in homologous DNA sequences that can be detected by the presence of fragments of different lengths after digestion of the DNA samples in question with specific restriction endonucleases. Twenty loci show distorted segregation, four of which are clustered on chromosome 4A and three on the 2D chromosome. The linkage maps of these RFLP loci have a total size of 1800 cM and exceed those of the classical genes in both size and locus number. In addition, the carrier chromosomes of 228 non-RFLP loci were identified. By nulli-tetrasomic analyses, all linkage groups were assigned to one another of the 21 wheat chromosomes. Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) is a technique that exploits variations in DNA sequences.DNA from differing sources will have variations or polymorphisms throughout the sequence.Using restriction enzymes, these differences in sequences may be teased out. Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) (pronounced rif lip) is one of the earliest molecular markers developed for genetic mapping and one of the. In total, 204 RFLP loci were identified and their linkage relationships established. duhamelianum (Spelta), exhibiting the greatest number of RFLPs among eight common wheats, were analyzed for their RFLP genotypes using genomic DNA clones of CS as probes. Sixty-six F2 plants from the cross, Triticum aestivum cv.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
